Step 1 - Setting up the store code for Dynamic Content
Now that you have an overview of the Dynamic Content feature, let's start the feature implementation by setting up your store code.
Instructions
1. Mapping pages and data-fetching functions
Create a file to map the home and landing Pages to their data-fetching functions. This file maps the home or the landing pages slug to a respective data fetch function, which will fetch, handle, and return the desired server-side data to display the content in a store section. For example, you can add an image from a third-party source in a Hero component.
-
Open your FastStore project in any code editor that you prefer.
-
In the
srcfolder, create thedynamicContentfolder. -
Inside the
dynamicContentfolder, create theindex.tsfile. -
Inside
index.ts, add the following code:- First, we define the
fetchDataMyLandingPage, which calls for an external API (https://fakestoreapi.com/products) to fetch the product information. - The
dataobject returns the information. - The
dynamicContentrelates the slug that we will define in the Headless CMS.
- First, we define the
Let’s dive deep into
dynamicContent and the pages allowed to be customized with the Dynamic Content feature: home and landing pages:dynamicContent
The
dynamicContent object stores key-value pairs:- The key represents the page slug (e.g.,
homefor the Home page andmy-landing-pagefor a specific Landing page). - The value is the corresponding data-fetching function responsible for fetching data for that page. In this example,
fetchDataMyLandingPage.
Home
This page is a singleton page, meaning it is unique in your store. This page is mapped using the key
home for the Dynamic Content feature. The value of the home key is a data-fetching function that returns the necessary data for the Home.Landing page
Landing pages can represent different pages and URLs. To identify the landing page, use the slug from the Headless CMS SEO Path input in the Settings tab as the key to the
dynamicContent object without the initial /. In the example below, the value /my-landing-page.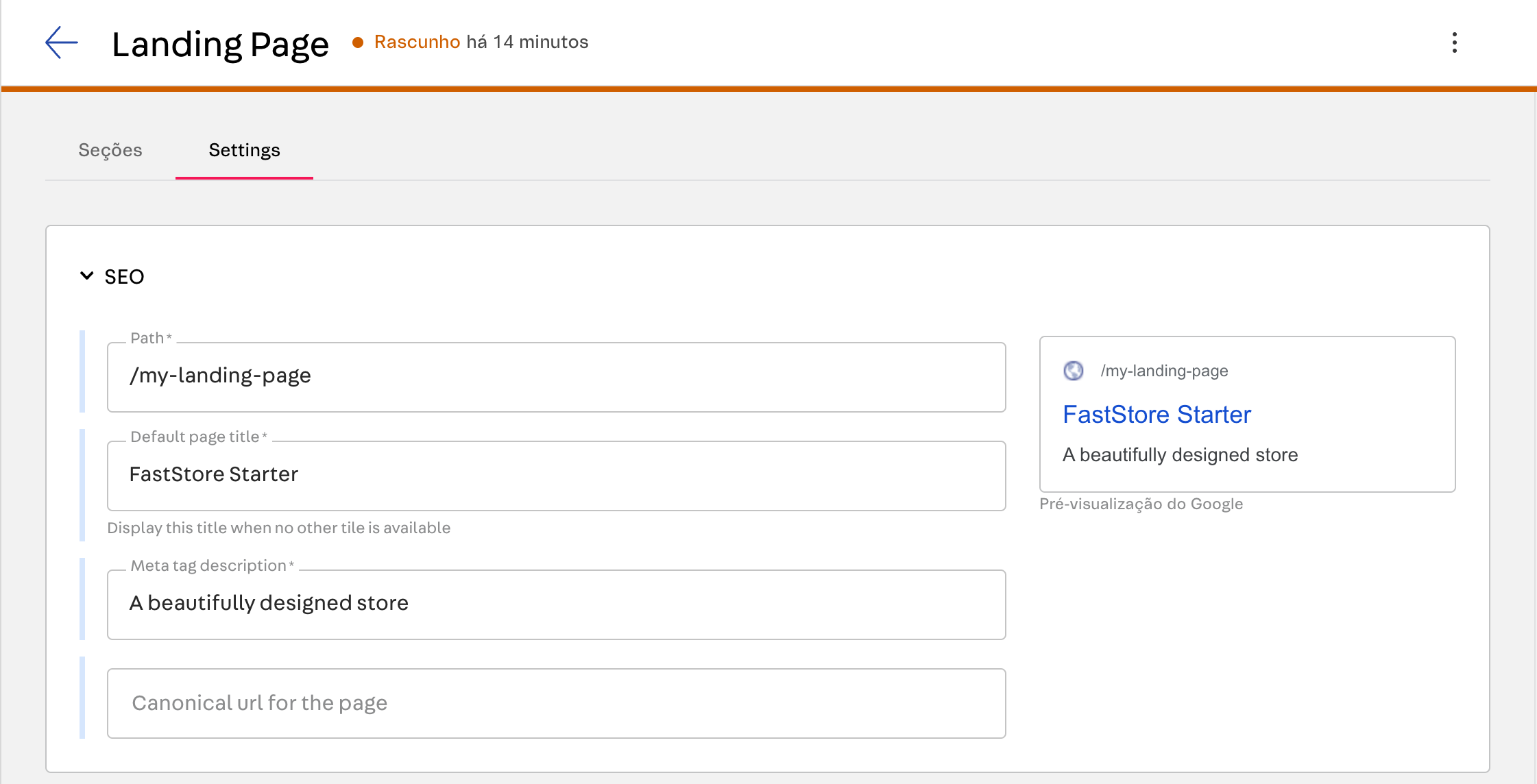
Now that we've established the file for mapping pages to data fetching functions let's define those functions to customize your component using third-party sources.
2. Creating Dynamic Content via API fetching
After mapping pages and data-fetching functions, you need to define these functions and create the logic to fetch the data from other data sources. There are two ways for fetching data:
- Using API extensions: Leverage the existing API Extension feature to fetch the data.
- Using fetch API or any requesting library: Request Fetch API or any HTTP library to directly fetch the data (Axios, fetch, etc).
Using API Extensions
-
In the store code, create the folder
graphqlin the' src' folder. -
Inside
graphql, create the folderthirdParty. This folder will contain the external data that we want to obtain. -
Create two other folders inside the
thirdParty:resolversandtypeDefs. -
Inside
typeDefscreate theextra.graphqlfile. -
Add the following code:
-
The field
ProductsExtraDatarepresents product data, with fields for id, title, price, description, category, image, and rating. -
The field
ExtraDatacombines a list ofProductsExtraDataand additional custom fields. -
The field
Querydefines queries for fetching extraData and namedExtraData.
Now, create the logic to fill these fields: -
-
Create a file called
query.tsinside the' resolvers' folder. -
Add the following code to it:
getProductsFromAPIfetches product data from an external API.extraDataresolves theextraDataquery by fetching and returning products.namedExtraDataresolves thenamedExtraDataquery by returning a custom message.
-
Create a file called
extra.tsinside the' resolvers' folder. -
Add the following code to it:
- The
Queryfunction returns the API data in the fieldextraDatathrough a request on an external API.
- The
-
Inside the
resolversfolder, create a file calledindex.tsand add the following code: -
Combine your resolvers and queries into the store's dynamic content in the
index.tsxfile inside thedynamicContentfolder.- Imports:
- Import
gqlfor defining GraphQL queries. - Import execute_unstable for running server-side GraphQL queries.
- Import
queryDefining the GraphQL Query:- Query named
ServerDynamicContentaccepts anameparameter. - Fetches fields under
extraDataincluding nestedrating. - Fetches
namedExtraDatabased on the name parameter.
- Query named
fetchDataUsingApiExtension:- It executes to run the GraphQL query with specified variables.
- Returns the result data or logs and returns an error if it fails.
dynamicContent:- Maps the slug
my-landing-page-api-extensionsto thefetchDataUsingApiExtension function. - This slug identifies in the code which content we want to bring to the page.
- Maps the slug
- Imports:
You can render this data in your store sections once you've set up your dynamic content fetching functions and mappings. See the Step 2 - Handling Dynamic Content within custom sections guide for more information on using this data in a new section.
Using Fetch API or any request library
Single request
You can use Fetch API to directly fetch data from an endpoint.
fetchDataMyLandingPage:- Fetches data from
https://fakestoreapi.com/products. - Returns the fetched data as an object with a data key.
- Fetches data from
Multiple Requests Example
Use
Promise.all to fetch data from multiple endpoints concurrently.fetchDataHomepage:- Concurrently fetches data from two endpoints.
- Returns the data from both endpoints in a single data object with separate keys for each product.
Once you've set up your dynamic content fetching functions and mappings, you can render this data in your store sections. For more information on using this data in a new section, see the Step 2 - Handling Dynamic Content within custom sections guide.
Returning the data Object
For both approaches, data fetching using Fetch API or Data Fetching using API extensions, the data-fetching function must return an object with data as the root key in the following format:
_10return {_10 data: {_10 // data fetched_10 },_10};
The data object can contain other objects inside:
_10return {_10 data: {_10 key1: result1,_10 key2: result2,_10 },_10};